Abstract
Background: The International Staging System (ISS) which has 2 components, serum albumin and beta-2 microglobulin, has been used effectively to prognosticate newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) since 2006 when it effectively replaced the Durie-Salmon staging system. In 2014, the International Myeloma Working Group proposed a system inclusive of ISS incorporating molecular markers and age (IMWG-2014). More recently, the revised- ISS (R-ISS) including ISS, high risk molecular markers and serum LDH at diagnosis has been proposed and validated in Europe. We hypothesized that the IMWG-2014 and R-ISS are more prognostic of outcomes than the ISS.
Methods: MM patients identified in the CIBMTR database who underwent first AHCT in 2008-2014 with high dose melphalan after novel therapy induction, within 18 months of diagnosis, and with available diagnostic LDH and molecular studies were included (n= 628). Patients were categorized into each of the 3 systems: ISS, IMWG-2014 and R-ISS. The relative risk of relapse/progression, progression-free survival and overall survival was calculated using the Cox proportional hazards regression with staging system as predictor. We computed a measure of separation (SEP) for the Kaplan-Meier curves, with larger numbers representing more separation. Agreement between the systems was determined using the kappa statistic.
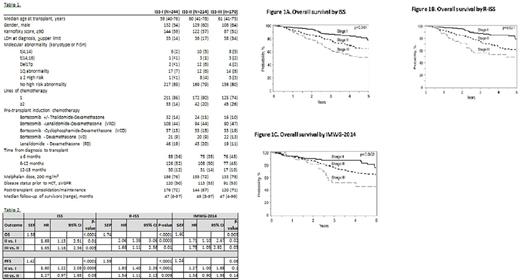
Results: The number of patients in each group were as follows: ISS I, N=244; ISS II, N=214) and ISS III, N=170, IMWG-14 low, N =130; standard N=451 and high N=47, and R-ISS stage I, N=199; R-ISS II, N=360 and R-ISS III, N=69. Table 1 shows the baseline characteristics of the cohort. Multivariate analysis comparing outcomes in this cohort using 3 prognostic models found statistically significant hazard ratios for PFS and OS when comparing stages in all models except for PFS when using the IMWG-2014 model (PFS 0.06) (Table 2). The SEP was 1.74 using the R-ISS, 1.60 using the IMWG-2014 and 1.58 using ISS for OS. For PFS, the SEP was 1.59 using R-ISS; 1.24 using the IMWG-2014 and 1.42 using ISS (Table 2). Greater separation was seen in the R-ISS survival compared to ISS and IMWG- 2014, which was also reflected in the higher hazard ratios. Figure 1 shows OS by ISS (1A), R-ISS (1B) and IMWG-2014 (1C). Upon measuring agreement between ISS and R-ISS, the weighted kappa statistic was 0.78 (95% CI 0.74-0.81) denoting good agreement between the 2 systems, but only 0.30 (95% CI 0.25-0.35) between ISS and IMWG-2014.
Conclusions: Although all 3 models are valuable, the R-ISS system provides the greatest degrees of separation between survival curves and thus most accurately delineates the differences between the 3 stages, followed by the ISS. R-ISS has good agreement with ISS.
Hari: Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Kumar: Celgene, Millennium/Takeda, Onyx, AbbVie, Janssen, Sanofi, Novartis, Amgen, Genentech, Merck, Oncopeptides, Roche, Skyline Diagnostics: Research Funding; Celgene, Millennium, BMS, Onyx, Janssen, Noxxon, AbbVie, Amgen, Merck, Oncopeptides, Skyline Diagnostics, Takeda: Consultancy; Skyline: Honoraria. Gasparetto: Janssen, BMS, Celgene: Consultancy; Celgene: Research Funding; Janssen, BMS, Celgene, Takeda: Honoraria; Janssen, BMS, Celgene: Other: Travel, accommodations, or other expenses paid or reimbursed. D'Souza: Celgene: Consultancy; Prothena: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.